Measuring crop yield
Estimating the yield of a brassica crop is critical for allocating the correct break size and animal allowance. Crop dry matter percentages are often assumed, and these can be very inaccurate.
Fresh weight
For leaf crops such as kale and rape join both ends of a 3.54 m length of alkathene to create a circle with an area of 1 m2. Place this over representative areas of the crop. To quantify the fresh weight, cut, bag and weigh everything within the circle. Remember to subtract the bag weight. For bulb crops sown in rows, like swedes, harvest part of a row. Row width will determine length sampled, e.g. for 50 cm wide rows, a 2 m row sample length will give an area of 1 m2.
In all situations
Repeat sampling at least 5 times across the paddock to gain an average fresh weight. The more variable a crop the more samples you need. The fresh weight is then multiplied by 10,000 to convert from kg/m2 to kg/ha (10,000 m2 = 1 ha)
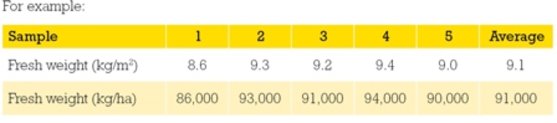
Dry matter %
Take three samples per crop to determine the dry matter percentage. For each sample, take 2 or more whole plants which are representative of the crop, and chop into small segments. Weigh the sample to determine fresh weight, then dry at 60-90ºC for 48 hrs, until the weight stops changing. Then weigh the dried sample.
The DM % can be calculated by dividing the dry weight by the fresh weight. Some labs offer DM testing.
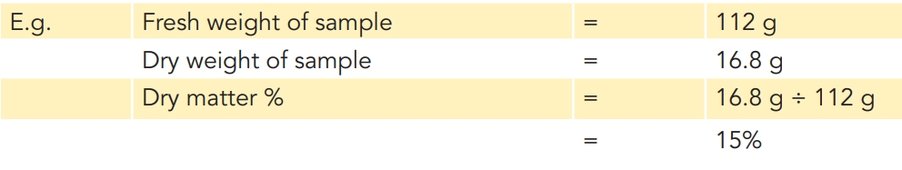
Crop yield (kg DM / ha)
Once you know the fresh weight yield (91,000 kg/ha) and the DM % (15%) you can calculate crop yield in kg DM per hectare.

Crop feed quality (ME)
You can’t calculate accurate feed allowances for your animals if you don’t know the quality of the crop they will be grazing. Send a representative sample to a laboratory to test quality, particularly metabolisable energy (ME). You can do this when you send samples for dry matter testing.

