Sowing ryegrass
Sowing date of grasses
Sowing date affects pasture persistence. Early autumn sowing is important in summer-dry areas, so plants have time to reach a robust size, prior to the following summer.
Autumn sowing date
In autumn, late sowing means slower establishment due to the cooler temperatures. Young plants then have less time to reach a robust size (e.g. grasses >20 tillers) to help their persistence, prior to the (potentially dry) summer. Sowing into dry conditions, prior to rain, and letting rain germinate seed can allow faster establishment than waiting for rain before sowing. In these conditions research has shown NEA2 endophyte survives well in the soil for up to 6 weeks prior to rain.
Some species, such as brome grasses and tall fescue, need warmer conditions than ryegrass to establish well, so must be sown early when soil temperatures are consistently >12°C. If farmers are serious about using these, programming a summer fallow to build up soil moisture, followed by direct-drilling, can greatly reduce the risk of poor establishment in dry autumns.
With later sowing and slower establishment, the potential to pug and damage new pastures in winter and spring is greater, because plants are smaller and weaker.
Spring sowing date
Spring pasture sowing requires reliable summer moisture for young pastures to establish, so cannot be reliably used in many regions. However, spring sowing is regularly undertaken in areas with good summer rainfall (e.g. Southland, the West Coast and some higher altitude areas), and irrigation (e.g. Canterbury and Otago).
Sowing date is a balancing act between getting new pasture in as soon as possible, but avoiding the risk of cold temperatures slowing establishment, which often leads to high weed content. As a general rule, wait until soil temperatures are >10°C before sowing ryegrass, and >12°C for brome grasses and tall fescue.
Seedbed consolidation
A level seedbed greatly improves pasture establishment, particularly for clover.
Seedling establishment
Seedbed consolidation conserves moisture and allows a seed drill to achieve the right sowing depth.
Research in the Manawatu showed sowing with a V-roller into a well-consolidated seedbed gave 50% better white clover and 25% better ryegrass establishment than sowing into a poorly consolidated seedbed.

In this case a Cambridge roller was weighted with concrete posts, to compact the soil until the roll form held under normal walking pressure. This research also highlighted the bad practice of using rubber wheeled rollers, which do not compact the soil well.
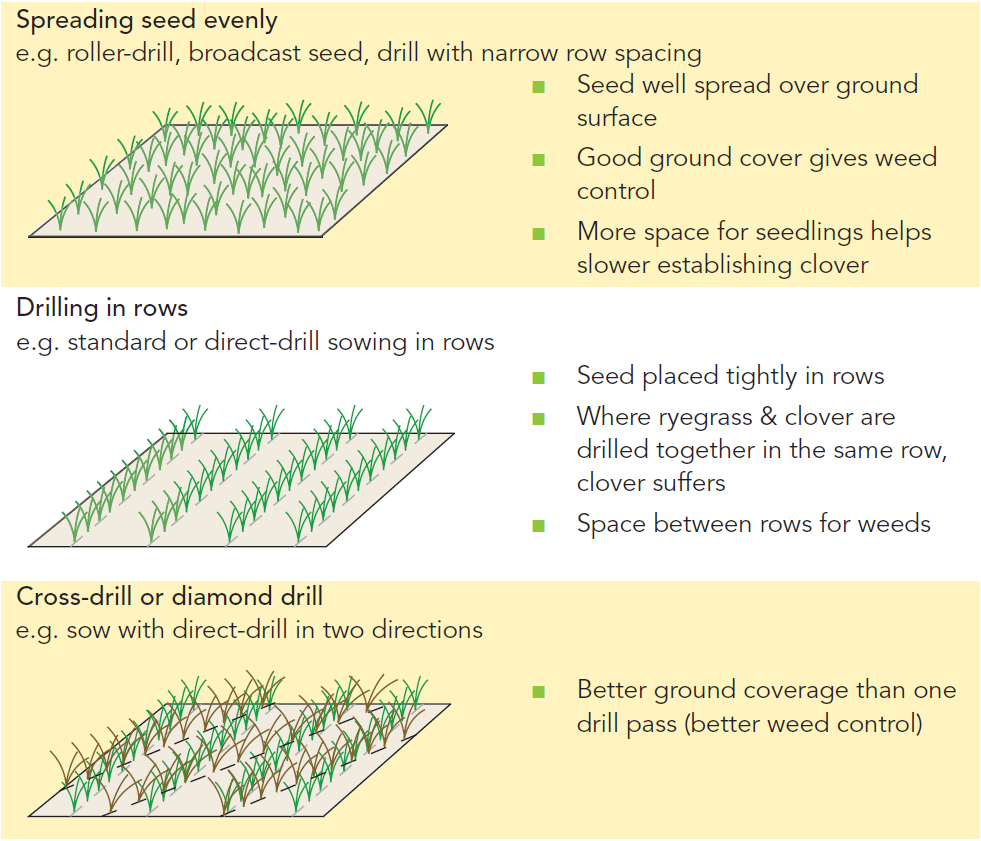
Drilling method
Drilling method is a critical decision when establishing a new permanent pasture. Good ground cover, or density, at sowing improves clover establishment and gives much better weed control.
Drilling Methods
Improve method
Sometimes a drill or drilling method can be modified to get better ground coverage. If row drilling, for example, remove the tubes from under the seed box so seed simply sprinkles on the ground. Welding a ^ shaped angle iron under seed box can help seed spread. If direct drilling, sprinkle clover seed and 1/4 of ryegrass seed through a small seed box (with tubes removed) ahead of the main drill. Main drill coulters will help cover and sow this seed.

Sowing depth
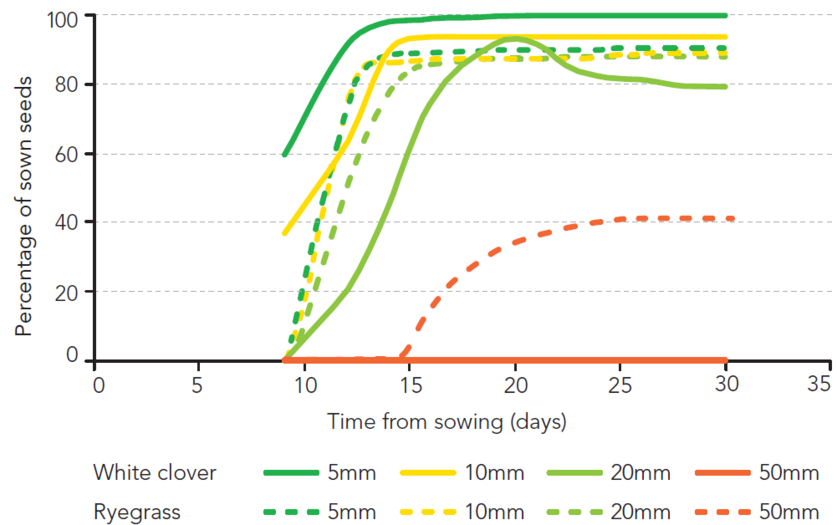
Sow ryegrass/white clover seed mixes at <10mm deep to get the best establishment. White clover seed is very small and sensitive to sowing depth and establishes much faster sown at this depth. Ryegrass is less sensitive to sowing depth and still establishes well sown at 20 mm. At 50 mm, neither species establishes well.
Dry conditions
The exception to sowing shallow is in dry conditions, when it is sometimes better to drill seed a little deeper into better soil moisture. In these conditions white clover may struggle, but seed can be spread on when conditions improve.
Consolidation
A consolidated seed bed is critical to allow good depth control with a seed drill. In a soft seedbed wheel tracks are pushed down, and coulter depths vary, leading to both uneven sowing depth and establishment. The same effects can occur when drilling too fast, causing uneven sowing depth.
Effect of sowing depth (mm) on ryegrass and clover establishment rate